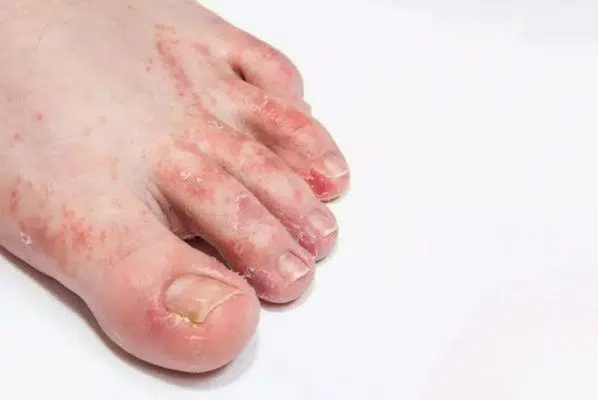
 Also known as Tinea Pedis, Athlete’s foot is a contagious fungal infection affecting feet skin, and can easily be spread to the toenails and the hands. As this condition is commonly seen in athletes, it is thereby called Athlete’s Foot. Although the condition is not that serious, sometimes it becomes hard to be cured. If one has diabetes or a weakened immune system and suspects to be suffering from Athlete’s foot, one is highly encouraged to immediately talk with one’s doctor.
Also known as Tinea Pedis, Athlete’s foot is a contagious fungal infection affecting feet skin, and can easily be spread to the toenails and the hands. As this condition is commonly seen in athletes, it is thereby called Athlete’s Foot. Although the condition is not that serious, sometimes it becomes hard to be cured. If one has diabetes or a weakened immune system and suspects to be suffering from Athlete’s foot, one is highly encouraged to immediately talk with one’s doctor.
What are the signs of Athlete’s Foot?
Tinea pedis, eczema, dermatitis, and psoriasis have common symptoms including red, itching, and burning feet, and red and flaky skin between the toes. However, among them, tinea pedis is the most common infection. It is also called the athlete’s foot.
Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection whose major transmission agent is the locker room and shower room, especially public ones. The fungus is responsible for the signs like redness, itching, and blisters between your toes.
What is Athlete’s Foot?
This is a fungal skin infection which is contagious. It mainly affects the feet, scalp, groin, and below the breasts. The infection is spread through towels, skin to skin contact, clothes, or washroom floors. The other name for athlete’s foot is ringworm, which is often misleading since worms are not involved. Just like all other fungal infections, tinea needs warm and moist environments. That is why it is most common in the warmest areas of the body. Communal showers and locker rooms are common agents of spreading the infection.
Types of Tinea:
The types of tinea are classified based on the part of the body they affect. Some of them include:
- Athlete’s foot- affects the foot. Also called tinea pedis.
- Jock itch- affects the groin and also called tines cruris.
- Ringworm of the scalp- affects the head and also called tinea capitis. It is common in children.
- Ringworm of the body (tinea corporis).
- Nail infection/ onychomycosis- affects the toes or fingernails. Also called tinea unguium.
Symptoms of Tinea
Its symptoms include:
- Itching and stinging
- Bald spots on the scalp.
- White or yellow discoloration of the nails
- Red scaly rash that is annular
- Blisters
How to avoid Tinea infection
Things like perspiration and overeating may cause tinea infections. To avoid it, the following are suggestions:
- Dry the skin well after showering, especially between the toes and other skin folds.
- Keep the skin exposed to the air often.
- Control excessive perspiration using antiperspirants.
- Instead of wearing synthetics, use cotton socks.
- Wear thongs to communal areas like gyms and locker rooms.
Treating a Tinea infection
Most tinea infections are treated using antifungal cream. However, others don’t respond well to the cream and might require antifungal tablets too.
Preventing the spread of Tinea
Since tinea is contagious, it is important to prevent its spread using measures that include the following:
- Treat the infection with antifungal cream.
- Wash your hands well after coming into contact with infected areas.
- Avoid walking barefooted if you have tinea pedis.
- Clean the shower room thoroughly after use.
- Avoid sharing towels.
